Home Medical Equipment (HME) providers operate in one of the most demanding segments of healthcare logistics. Unlike traditional retail or even standard medical supply chains, HME delivery requires precision, regulatory awareness, empathy, and operational excellence. Patients rely on timely and accurate deliveries of oxygen concentrators, hospital beds, mobility aids, CPAP machines, and other life-sustaining devices. Any delay, error, or miscommunication can directly affect patient outcomes.
This is why hme delivery management has become a strategic priority for modern HME businesses. It is no longer just about moving equipment from a warehouse to a home. It is about orchestrating people, processes, technology, and compliance into a seamless delivery experience that supports both patients and providers.
In this in-depth guide, we will explore what HME delivery management is, why it matters, its core components, common challenges, best practices, and future trends shaping the industry.
What Is HME Delivery Management?
HME delivery management refers to the structured coordination of all activities involved in delivering, installing, maintaining, retrieving, and tracking home medical equipment. This includes:
-
Order intake and scheduling
-
Inventory allocation
-
Route planning and dispatch
-
Delivery and setup at the patient’s home
-
Staff training and certification tracking
-
Documentation and proof of delivery
-
Equipment pickup, cleaning, and refurbishment
Effective hme delivery management ensures that the right equipment reaches the right patient, at the right time, in the right condition, while complying with healthcare regulations and payer requirements.
Why HME Delivery Management Is Critical in Healthcare
Unlike standard logistics, HME delivery is tightly connected to patient safety and clinical outcomes. A missed delivery of oxygen equipment or a delayed hospital bed installation can lead to severe health risks, hospital readmissions, or dissatisfied referral partners.
Here are the key reasons why hme delivery management is so critical:
1. Patient-Centered Care
Patients receiving HME are often elderly, disabled, or recovering from illness or surgery. They depend on punctual delivery, professional setup, and clear instructions. A well-managed delivery process enhances trust and comfort.
2. Regulatory Compliance
HME providers must comply with healthcare regulations, payer rules, and accreditation standards. Proper delivery documentation, staff credentials, and equipment tracking are essential to avoid audits and penalties.
3. Operational Efficiency
Fuel costs, labor shortages, and rising operational expenses make inefficiencies extremely costly. Optimized delivery management reduces waste, missed appointments, and unnecessary re-deliveries.
4. Financial Performance
Accurate deliveries, proper documentation, and timely pickups directly impact billing cycles, reimbursement, and cash flow.
Core Components of HME Delivery Management
To fully understand hme delivery management, it helps to break it down into its essential components.
Order Intake and Scheduling
The process begins when an order is received from a hospital, physician, discharge planner, or directly from a patient. This step includes:
-
Verifying patient information
-
Confirming insurance and authorization status
-
Determining delivery urgency
-
Scheduling delivery windows
Errors at this stage can cascade throughout the entire workflow.
Inventory and Equipment Allocation
HME providers must ensure the correct equipment model, size, and accessories are available before dispatch. This includes:
-
Real-time inventory visibility
-
Equipment condition tracking
-
Maintenance and cleaning status
-
Serialized asset management
Without proper coordination, drivers may arrive with incorrect or unavailable equipment.
Route Planning and Dispatch
Route optimization is a cornerstone of efficient hme delivery management. Dispatchers must balance:
-
Geographic delivery zones
-
Delivery time windows
-
Driver skills and certifications
-
Equipment size and vehicle capacity
Smart route planning reduces fuel consumption, improves on-time performance, and lowers driver stress.
Delivery, Setup, and Patient Education
HME delivery is not just drop-off. It often includes:
-
Equipment assembly and installation
-
Safety checks
-
Patient and caregiver education
-
Documentation and signatures
Drivers and technicians serve as the face of the company and play a key role in patient satisfaction.
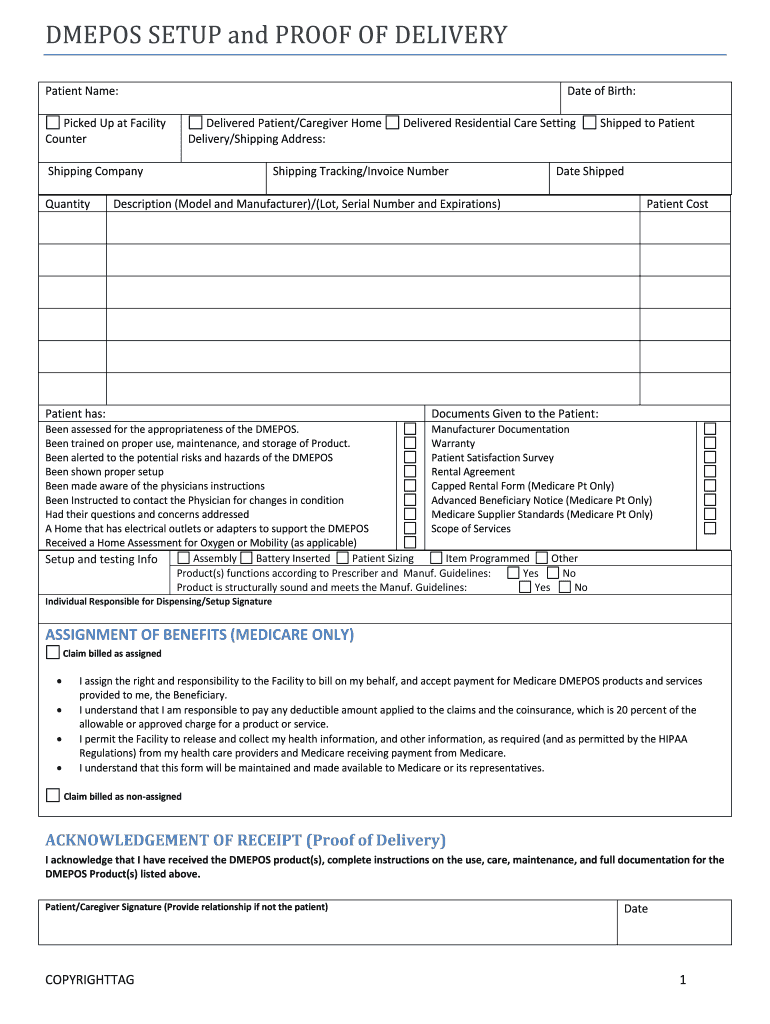
Proof of Delivery and Documentation
Accurate documentation is vital for compliance and reimbursement. This may include:
-
Digital signatures
-
Time-stamped photos
-
Setup confirmation forms
-
Driver notes
Strong hme delivery management ensures documentation is captured correctly and stored securely.
Equipment Pickup and Reverse Logistics
When equipment is no longer needed, providers must coordinate pickup, cleaning, inspection, and redeployment. Reverse logistics is often overlooked but is critical for asset utilization and cost control.
Common Challenges in HME Delivery Management
Even experienced HME providers face recurring challenges that can strain operations.
Missed or Failed Deliveries
Patients may not be home, addresses may be incorrect, or schedules may change unexpectedly. Each failed delivery increases costs and delays care.
Limited Visibility
Without real-time tracking, dispatchers and customer service teams struggle to answer simple questions like “Where is my delivery?”
Manual Processes
Paper-based delivery tickets, phone calls, and spreadsheets create inefficiencies, errors, and data silos.
Workforce Constraints
Driver shortages, high turnover, and inconsistent training affect service quality and reliability.
Compliance Risks
Incomplete documentation or unqualified staff performing setups can trigger audits, denied claims, or legal exposure.
Best Practices for Effective HME Delivery Management
1. Standardize Delivery Workflows
Define clear, repeatable processes for order intake, scheduling, delivery, and pickup. Standardization reduces errors and improves scalability.
2. Invest in Staff Training
Drivers and technicians should be trained not only on equipment handling but also on patient interaction, safety protocols, and documentation requirements.
3. Use Real-Time Tracking
GPS tracking and live status updates provide transparency for both staff and patients, improving communication and trust.
4. Prioritize Patient Communication
Automated reminders, estimated arrival times, and follow-up messages reduce missed appointments and enhance the patient experience.
5. Monitor Performance Metrics
Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as on-time delivery rate, first-attempt success rate, and cost per delivery help identify improvement areas.
By applying these best practices, hme delivery management becomes a strategic advantage rather than a daily struggle.
The Role of Technology in HME Delivery Management
Technology has transformed how HME providers manage deliveries. Modern solutions integrate multiple functions into a single ecosystem, enabling smarter decision-making and automation.
Key technological capabilities include:
-
Delivery scheduling and dispatch dashboards
-
Route optimization algorithms
-
Mobile apps for drivers
-
Digital proof of delivery
-
Equipment lifecycle tracking
-
Reporting and analytics
When implemented correctly, technology reduces administrative burden and improves consistency across operations.
Impact on Patient Satisfaction and Referral Relationships
Hospitals, clinics, and discharge planners prefer working with HME providers who consistently deliver on time and communicate clearly. Strong hme delivery management directly affects:
-
Referral volume
-
Contract renewals
-
Online reviews and reputation
-
Long-term patient loyalty
In a competitive market, reliability and professionalism often matter more than price alone.
Scaling HME Operations with Strong Delivery Management
As HME businesses grow into new territories or service lines, delivery complexity increases. Without scalable delivery management processes, growth can quickly lead to chaos.
A scalable approach includes:
-
Centralized scheduling with local flexibility
-
Data-driven route planning
-
Standardized training programs
-
Unified reporting across locations
This ensures consistent service quality regardless of size or geography.
Future Trends in HME Delivery Management
The future of hme delivery management will be shaped by several key trends:
Increased Automation
AI-driven route optimization and automated scheduling will further reduce manual effort.
Greater Patient Transparency
Patients will increasingly expect real-time delivery tracking similar to retail experiences.
Integration Across Healthcare Systems
Closer integration with electronic medical records and hospital discharge systems will streamline order flow.
Focus on Sustainability
Fuel-efficient routing and optimized asset utilization will support cost control and environmental goals.
Conclusion
HME delivery management is no longer a back-office function—it is a core pillar of successful home medical equipment operations. From patient safety and compliance to cost control and growth, every aspect of an HME business is influenced by how well deliveries are managed.
By investing in structured processes, trained staff, and modern technology, providers can transform hme delivery management into a competitive advantage. In a healthcare environment where expectations continue to rise, efficient and compassionate delivery is not optional—it is essential.